Health is a fundamental aspect of human existence, encompassing physical, mental, and social well-being. Good health enables individuals to lead productive and fulfilling lives. The importance of health cannot be overstated as it directly impacts quality of life and longevity. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the various dimensions of health, its significance, and ways to maintain optimal health throughout life.
The Multifaceted Nature of Health
Health is not merely the absence of disease; it is a dynamic state of complete physical, mental, Balanced Life and social well-being. Physical health involves the proper functioning of the body, enabling individuals to perform daily activities efficiently. Mental health refers to cognitive and emotional stability, allowing individuals to cope with stress and make sound decisions. Social health emphasizes healthy relationships and social interactions, fostering a sense of belonging and support.
The Significance of Health in Daily Life
Health plays a pivotal role in every aspect of life. Good health enhances productivity, enabling individuals to work effectively and achieve their goals. It reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. Mental health contributes to emotional resilience, enhancing the ability to handle challenges and maintain positive relationships. Social health promotes community engagement, creating a supportive environment for personal and collective growth.
Key Factors Influencing Health
Several factors influence health, including genetics, lifestyle choices, environment, and access to healthcare. Genetics determine predisposition to certain health conditions. Lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and sleep, significantly impact physical health. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients, while regular exercise improves cardiovascular health and strengthens muscles. Adequate sleep rejuvenates the body and mind, enhancing overall health.
Environmental factors, such as air quality and sanitation, affect health. Access to healthcare ensures timely diagnosis and treatment, preventing complications and promoting recovery. Social determinants, including education, income, and employment, also influence health outcomes.
Nutrition and Health
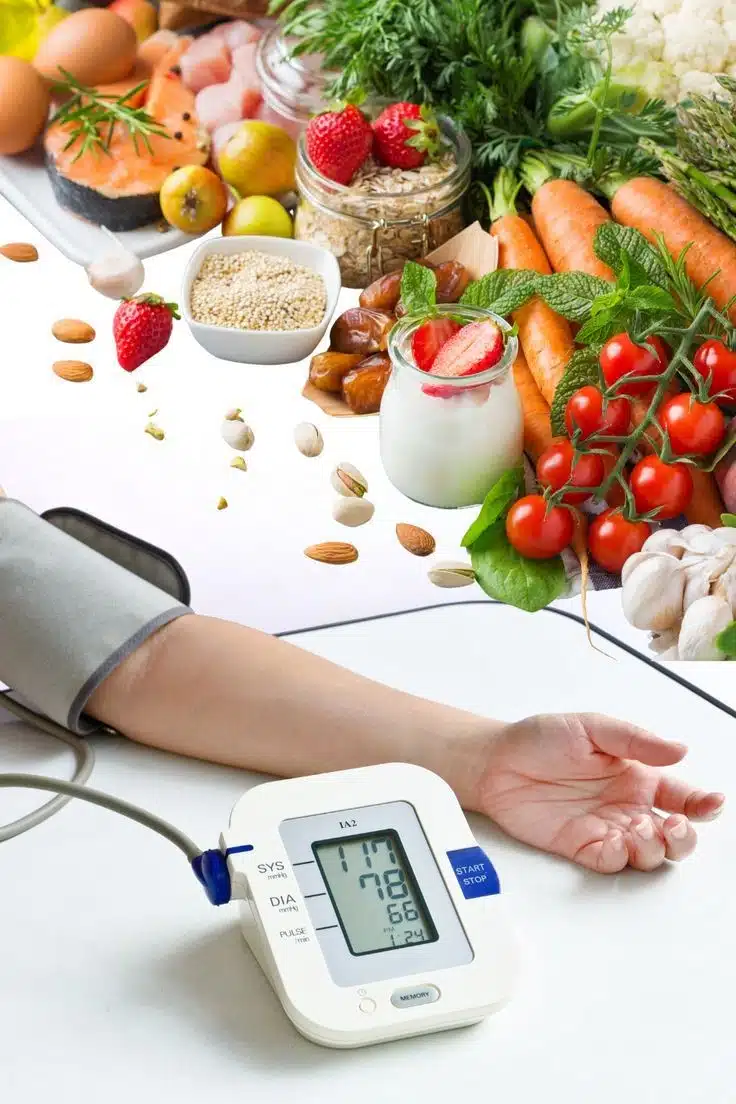
A nutritious diet is vital for maintaining good health. Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential vitamins and minerals. Hydration is equally important; drinking sufficient water supports bodily functions and prevents dehydration. Limiting processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats reduces the risk of obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Proper nutrition enhances energy levels, boosts immunity, and supports overall health.
Exercise: A Pillar of Health
Regular physical activity is crucial for sustaining health. Exercise strengthens the heart, improves circulation, and enhances lung capacity. It aids in weight management, reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions. Exercise also releases endorphins, improving mood and reducing stress. Incorporating activities like walking, jogging, swimming, or yoga into daily routines promotes physical and mental health.
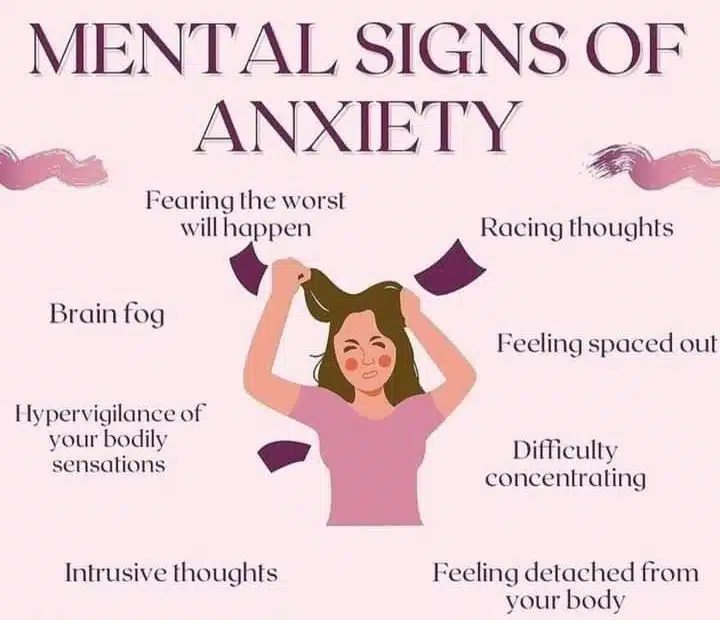
Mental Health: The Unsung Hero
Mental health is often overlooked but is integral to overall health. Psychological well-being impacts decision-making, relationships, and productivity. Stress, anxiety, and depression can adversely affect health, leading to physical ailments. Practicing mindfulness, meditation, and seeking professional support can enhance mental health. Open communication and strong support systems foster emotional stability and resilience.
Preventive Healthcare: Safeguarding Health
Preventive healthcare focuses on averting illnesses through early detection and proactive measures. Regular health check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings detect potential health issues early. Adopting healthy habits, such as handwashing and safe food practices, prevents infections. Health education empowers individuals to make informed choices, promoting long-term health.
The Role of Sleep in Health
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining health. Sleep allows the body to repair tissues, consolidate memories, and regulate hormones. Insufficient sleep can lead to fatigue, impaired cognitive function, and weakened immunity. Creating a sleep-friendly environment and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule supports restful sleep, enhancing overall health.
Stress Management for Health
Chronic stress negatively impacts health, increasing the risk of heart disease, hypertension, and mental health disorders. Effective stress management techniques, such as deep breathing, exercise, and hobbies, alleviate stress. Balancing work and leisure, setting realistic goals, and seeking social support contribute to stress reduction, promoting health.
The Interplay Between Health and Relationships
Healthy relationships positively influence health. Supportive family and friends provide emotional security, reducing stress and enhancing mental health. Social connections promote a sense of belonging, improving overall well-being. Conversely, toxic relationships can lead to anxiety and depression, underscoring the importance of nurturing positive relationships for health.
Technology and Health
Advancements in technology have revolutionized healthcare, improving diagnosis, treatment, and access to information. Telemedicine facilitates remote consultations, ensuring timely medical advice. Wearable devices monitor health metrics, encouraging proactive health management. However, excessive screen time can lead to digital eye strain and sedentary lifestyles, necessitating mindful technology use for health.
Health Across Different Life Stages
Health needs vary across life stages. Children require proper nutrition and immunization for growth and development. Adolescents need guidance on mental health, reproductive health, and healthy habits. Adults benefit from regular exercise, balanced diets, and stress management. Older adults require preventive care, mobility support, and chronic disease management to maintain health.
Cultivating Healthy Habits
Developing healthy habits is essential for sustaining health. Establishing a balanced routine encompassing nutritious meals, exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management fosters overall well-being. Avoiding harmful habits, such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, reduces health risks. Consistency and perseverance in adopting healthy behaviors contribute to long-term health.
The Global Perspective on Health
Health is a global priority, with organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) working towards universal health coverage and disease prevention. Global health challenges, such as pandemics, require collaborative efforts for effective responses. Promoting health equity ensures access to quality healthcare for all, regardless of socio-economic status.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Health for a Fulfilling Life
Health is the cornerstone of a fulfilling and productive life. Embracing a holistic approach that encompasses physical, mental, and social well-being promotes overall health. Nutrition, exercise, mental health, preventive care, and healthy relationships collectively contribute to optimal health. By prioritizing health, individuals can achieve their full potential and lead enriched lives.